Highlights of the Year
Highlight of Research & Development Studies
Study on Using Big Data-AI Technology in Real-time Environmental Monitoring under the Relocation of Sha Tin Sewage Treatment Works to Caverns Project
The study aims to apply Big Data and AI technologies (e.g. Deep Learning) to real-time environmental monitoring of egrets’ activity, noise levels and vibration conditions in the vicinity of the construction site of the Relocation of Sha Tin Sewage Treatment Works to Cavern Project, thereby creating a Big Data-AI analytic framework for realtime environmental monitoring in different stages of the project.
Application of Eco-landscape Design in DSD’s Facilities
In support of the Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan, DSD is exploring ways of eco-landscape planning, design and management to suit the Department’s facilities, with a view enhancing the landscape design of the facilities, increasing ecological value and refining the connectivity of ecological networks in the city.
Therefore, the University of Hong Kong was commissioned in 2017 to carry out study through which an indicator was devised to evaluate the potential ecological value of DSD’s facilities and serve as a reference guide to strategic landscape planning. The study will also provide suggestions for drawing up a code of practice on ecolandscape design and management; site trials will be carried out to assess its effectiveness.
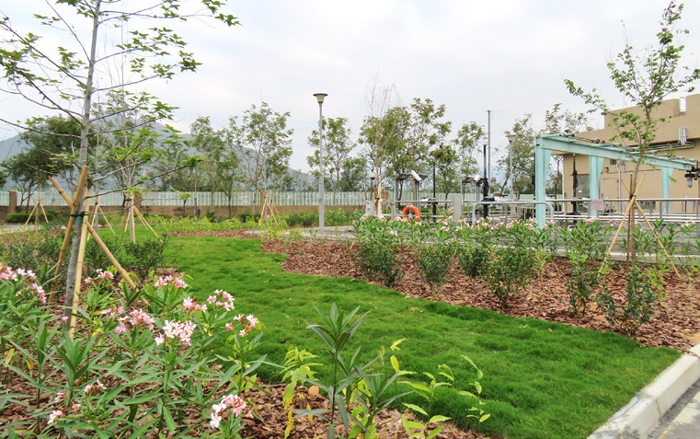

Application of Eco-landscape Design in DSD’s Facilities: Trial site at Ngau Tam Mei Main Drainage Channel Pumping Station
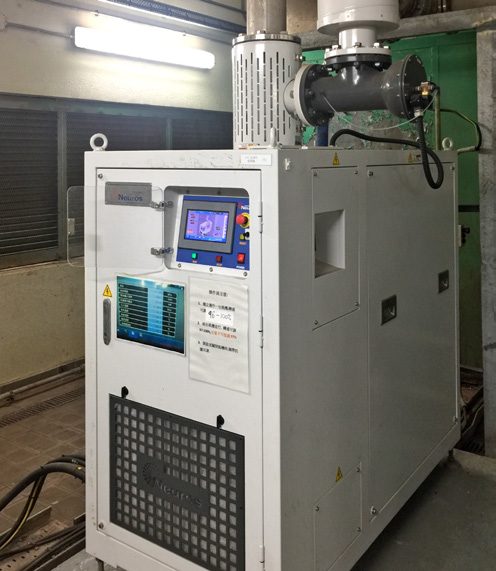
Using Air-bearing Type High Speed Centrifugal Air Blowers in Stanley Sewage Treatment Works
Aeration is crucial for sustaining the growth of micro-organisms in a biological sewage treatment process and breaking down pollutants in sewage. In general, aeration accounts for 40% of a sewage treatment works’ power consumption.
Compared with conventional air blowers, air-bearing blowers are more energy efficient. In 2018, DSD completed an R&D trial on air-bearing blowers at Stanley STW. Two conventional air blowers in Stanley STW were replaced with air-bearing blowers whose subsequent performance was closely monitored.
It was found that the air-bearing blowers produced less noise and heat and required less maintenance. Their energy consumption was approximately 22% lower than that of the replaced blowers and that a total of approximately 300,000 kilowatt-hours of electricity per annum was saved. After the trial, more air-bearing blowers have been installed at facilities such as Shek Wu Hui STW and Stonecutters Island STW.
Thin-film Solar Panels
In 2018, DSD completed a trial on different types of thin-film solar panels to gauge their performance, reliability and durability at Stonecutters Island STW and Sha Tau Kok STW. The test objects included types of thin film solar panels such as copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS), cadmium telluride (CdTe) and amorphous silicon (a-Si).
The test results revealed that CIGS panels were the most efficient ones and that the electricity output of thin-film panels installed in a vertical position was 20% less than those installed in a horizontal position.
Subsequent to the trial, DSD installed about 120 pieces of flexible CIGS thin film solar panels, which can provide an electricity output of about 14 kilowatts, on the covers of the sedimentation tanks at Stonecutters Island STW.