Innovative Technology for Sewage Treatment
In the past five years, the DSD treated a total of about 5.1 billion cubic metres of sewage. To facilitate Hong Kong's development and provide world-class sewage treatment services in the light of limited land resources, we have to apply innovative technologies to our work. Having conducted trials on various technologies that are helpful in improving sewage treatment efficiency, the DSD plans to apply these technologies in our future sewage treatment facilities.
Aerobic Granular Sludge Technology
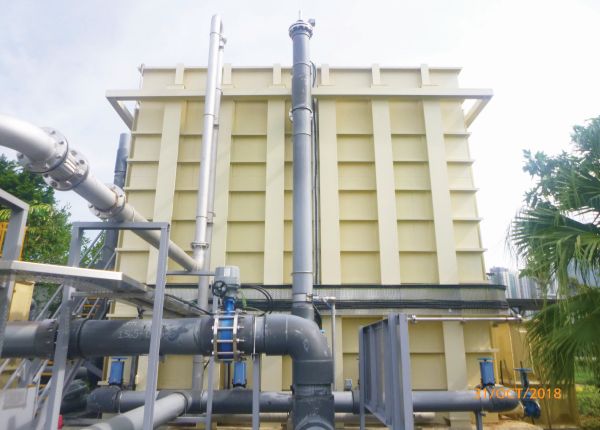
The Aerobic Granular Sludge (AGS) technology allows simultaneous removal of organic carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and other pollutants in a single treatment reactor. Compared with the conventional activated sludge process that relies on suspended biomass for sewage treatment, the AGS technology, which utilises granular sludge with a fast settling ability is more effective in treating sewage, giving us the advantages of a smaller footprint and lower energy requirements.
In 2019, the DSD completed a trial application of the AGS, the results of which demonstrated that the AGS technology was capable of meeting the effluent discharge standards under different loading and operating conditions. We will consider applying this promising technology to sewage treatment plants in the future.
Aerobic Granular Sludge Reactor
Membrane Bioreactor
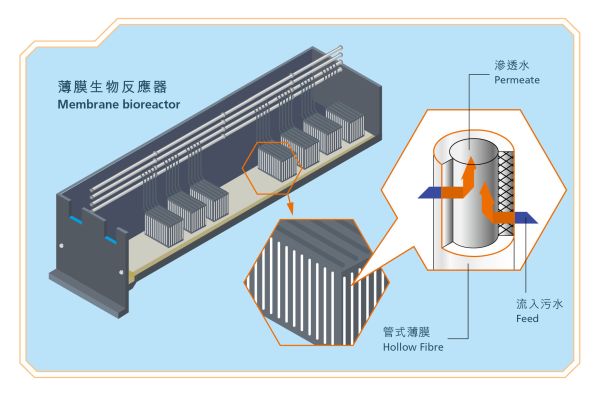
Membrane bioreactor (MBR) is a compact sewage treatment technology that can combine the suspended growth biological treatment process with the membrane liquid-solid separation process. Unlike the conventional sedimentation technology, the MBR technology, as a means of liquid-solid separation, can separate the permeate from the high concentration of mixed liquor within a very short period of time. Hence, compared with the ordinary bioreactor of the same size, the MBR can treat a higher volume of sewage. The membrane pore sizes are classified into microfiltration (MF) (100 to 5,000 nanometres), ultrafiltration (UF) (10 to 100 nanometres), nanofiltration (NF) (1 to 10 nanometres) and reverse osmosis. Membranes with a pore size equal to or smaller than UF can filter out many types of virus and bacterium, including E. Coli. The MBR will be used on a massive scale in Shek Wu Hui Effluent Polishing Plant for sewage treatment and the treated effluent will reach tertiary treatment level. Such effluent, after chlorination and disinfection, can be used as reclaimed water for purposes such as toilet flushing.
Membrane Bioreactor
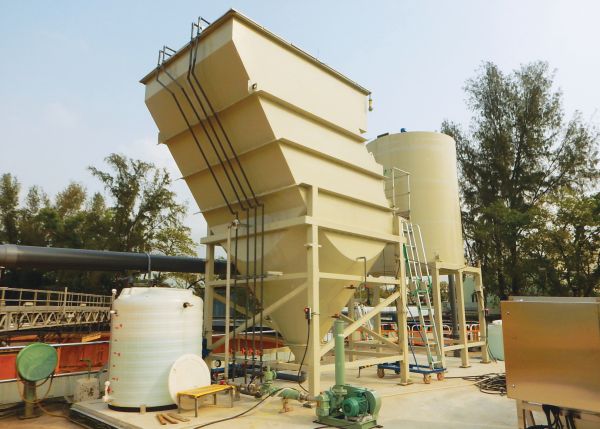
Inclined Plate Settler
The DSD completed a small-scale trial on the inclined plate settler in 2019 to evaluate its performance, robustness as well as operation and maintenance requirements when it was operating in the primary sedimentation tank. The treatment unit put to the test consisted of an inclined and rectangular separator tank with its hopper at the bottom for sludge discharge. The key feature of the unit is that the inclined plate installed at an angle of 55 degrees can allow maximum surface area for primary sludge to settle. Compared with the traditional primary sedimentation tank, the inclined plate settler requires a smaller footprint. Results of the trial were satisfactory, with the anticipated total suspended solids removal rate achieved, irrespective of whether there was any chemical dosing in the treatment process. This technology will be adopted in the Shek Wu Hui and Yuen Long Effluent Polishing Plants.
Inclined plate settler
Study of Using Two-point Chlorine Dosing
Under a study project on the disinfection facilities of the Harbour Area Treatment Scheme, the DSD applied chemical dosing at different locations inside the Flow Distribution Chamber of Stonecutters Island STW to study the efficiency of disinfectant mixing with sewage. The result showed that the efficiency of mixing could be effectively enhanced by dosing sewage with sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) in the high turbulent flow region at the overflow weir, with the chemical consumption substantially reduced by 20%, thereby minimising the consumption of chemicals for optimal disinfection.
Installation of chemical dosing unit at overflow weir of Flow Distribution Chamber
Physical model for testing the effectiveness of dosing sewage with sodium hypochlorite at different locations